Hyundai Accent: Tire Pressure Monitoring System / TPMS Receiver
1.FunctionThe TPMS monitors the pressure and temperature of the tires and warns the driver of changes that could potentially influence driving conditions.The cluster warning lamp displays the messages generated from processing the data. The ECU processes the data received from the WE sensor, determines the conditions of the tire, and then sends any necessary warning signals to the driver through the CAN line or hard wire control line.
2.Mode
(1)Virgin Mode
• This mode is active when a unit is stocked as a part for after-sales service, meaning that there is no data concerning the vehicle code, wheel size, and sensor ID stored in its memory.
• In this mode, the receiver does not save any RF signals it receives from the pressure sensors, nor does it control the warning lamp.
• It also does not detect or memorize DTCs, and it does not perform the Auto Learning and Auto Location functions.
• After turning the ignition on, use a diagnostic instrument (GDS etc.) or TPMS exciter to enter the vehicle code/wheel size/sensor ID. This changes the current mode to Normal.
(2)Normal Mode
• This is the mode applied when the vehicle is shipped from the factory.
• It performs all of the standard TPMS functions.
• Check the system warning lamp (TPMS lamp) to determine the current mode of the TPMS receiver.
• In virgin mode: When the IG turns ON, it remains ON for 3 seconds and then blinks every half second.
• In normal mode: When the IG turns ON, it remains ON for 3 seconds and then turns OFF. (However, it remains ON if a DTC exists.)
1.General Function
• Auto-locate/learn takes place only once per Ignition cycle.
• On successful completion, 4 road wheel sensor ID's, together with their respective road wheel positions are latched into memory for monitoring.
• Until Auto-learn completes, previously learned sensors (together with their respective locations) are monitored for under inflation / leak warnings.
• Spare tire inflation / DTC state is not displayed.
2.General Conditions to Learn New Sensors:
• Receiver must Auto-Locate 4 road sensors.
• Auto-location / learning only functions when speed is more than 20 kph (approx. 15 mph).
• Receiver must determine that it is confident that sensor is not temporary:
a.Uses vehicle speed.
b.Uses confidence reduction of previously learned sensors.
• Typical time at driving over 20 kph to learn a new sensor is up to 10 minutes.
3.General Conditions to Un-Learn a sensor that is removed:
• It takes less than 10 minutes at 20-30kph.
• Confidence reduction is dependant on vehicle speed and the number of sensors known to the receiver.
1.Disconnect the negative (-) battery cable.
2.Remove the crash pad.(Refer to Body - "Crash Pad")
3.Remove the connector.
4.Remove the bracket (B) and receiver (C) by loosening the nut (A).
Tightening torque :3.9 - 5.9 N.m (0.4 - 0.6 kgf.m, 2.9 - 4.3 lb-ft)
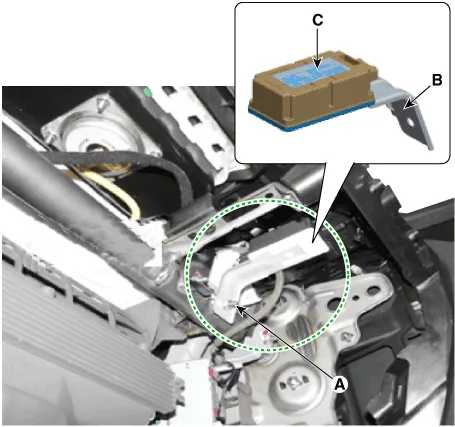
5.Install in the reverse order of removal.
6.Re-connect the battery, and then turn on the ignition.

• Firmly fasten the receiver connector until you hear a click.
7.Replace the receiver, and then perform the learning process using a diagnostic instrument (GDS).
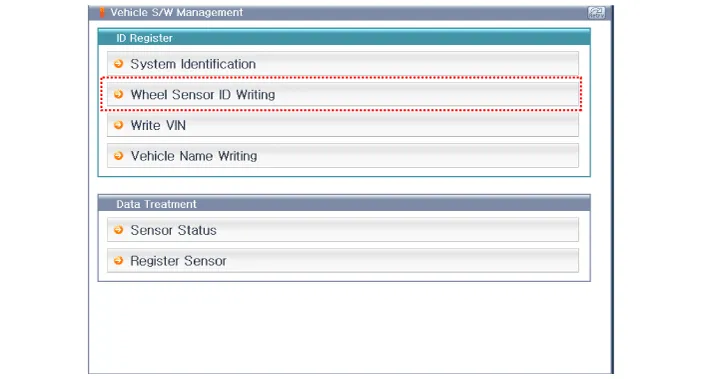
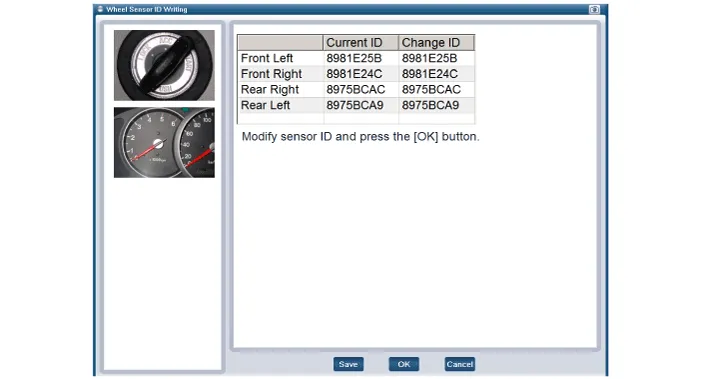
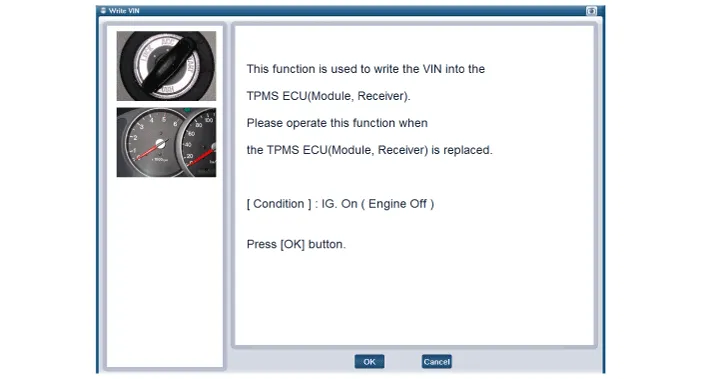
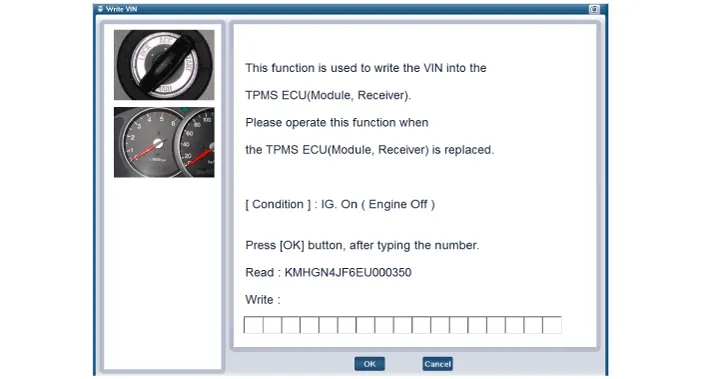
1.Connect the diagnostic instrument to the self-diagnostic connector (16-pin) beneath the crash pad on the side of driver's seat, and then turn on the ignition to activate the diagnostic instrument.
2.In the GDS Vehicle Type Selection menu, select "Vehicle Type" and "TPMS" System, and then opt for "OK."
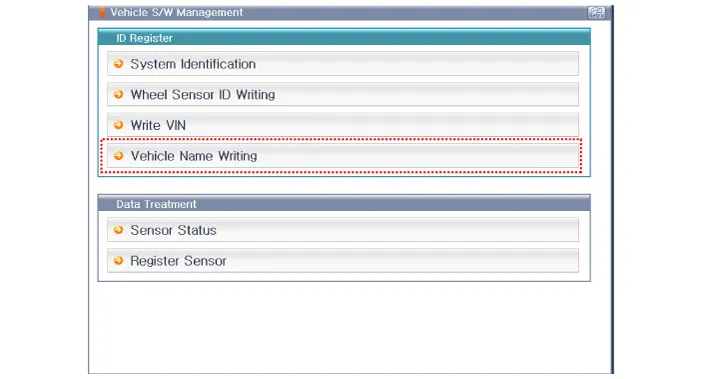
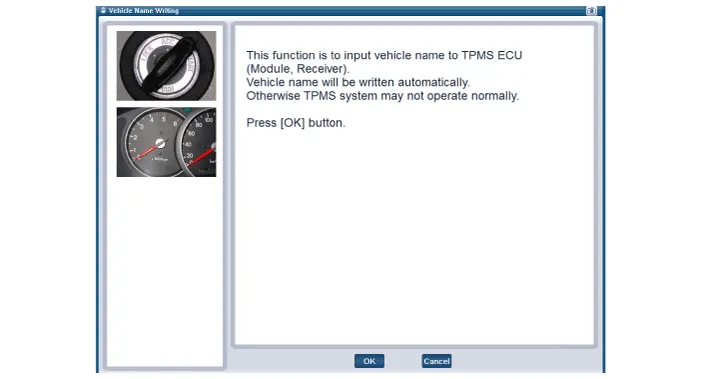
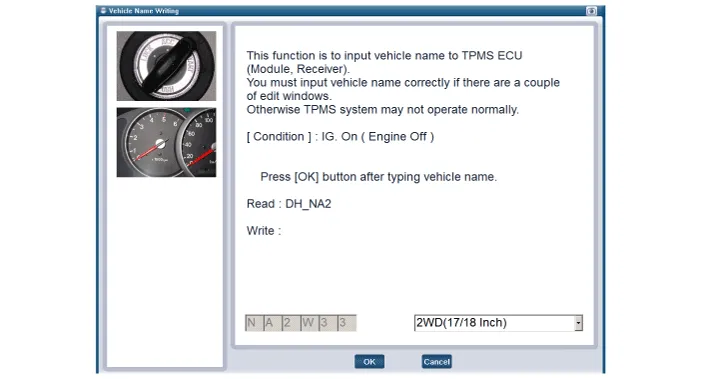
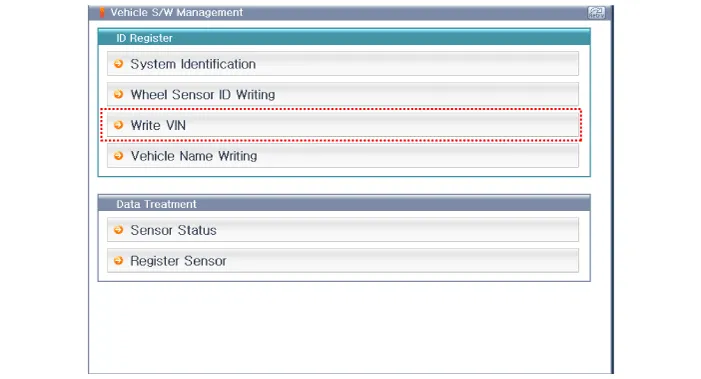
Other information:
Hyundai Accent (HC) (2017 - 2022) Service Manual: Specifications
- Specification EngineTransaxleJoint type Max. permissible angle OuterInnerOuterInner GAMMA 1.6AT / MTBJ#22TJi#2246.5°23° - Tightening torque Item N.mkgf.mlb-ft FrontHub nuts107.9 - 127.511.0 - 13.079.6 - 94.0 Driveshaft caulking nut274.6 - 294.228.0 - 30.0202.5 - 217.0 Strut assembly to knuckle98.1 - 117.710.0 - 12.072.3 - 86.8 Front caliper to knuckle78.Hyundai Accent (HC) (2017 - 2022) Service Manual: Variable Force Solenoid (VFS)
- Description CVVT (Continuous Variable Valve Timing) system advances or retards the valve opening and closing timing of the intake or the exhaust valve in accordance with the ECM control, calculated by the engine speed and the load. The CVVT control causes a valve over-lap or under-lap between the intake valve and the exhaust valve. This improves fuel efficiency, reduces exhaust gases (NOx, HC) and enhances the engine performance, thanks to reduced pumping loss, internal EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) release, improved combustion stability, and increased volumetric efficiency.
Categories
- Manuals Home
- Hyundai Accent Owners Manual
- Hyundai Accent Service Manual
- New on site
- Most important about car


