Hyundai Accent (HC): Emission Control System / Exhaust Emission Control System
Contents:
Catalytic Converter
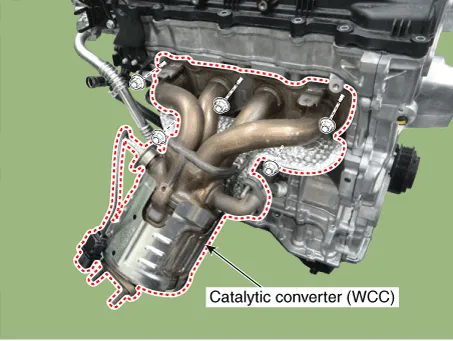
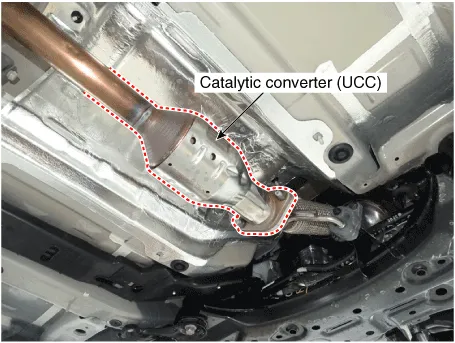
1.Remove the exhaust manifold.(Refer to Engine Mechanical System - "Exhaust Manifold")
1.Remove the catalytic converter & center muffler.(Refer to Engine Mechanical System - "Muffler")
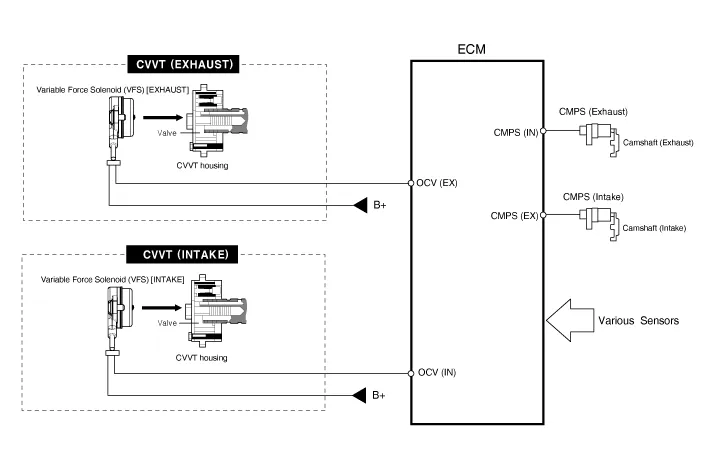
CVVT (Continuously Variable Valve Timing) System
– the CVVT Oil Control Valve (OCV) which supplies the engine oil to the cam phaser or takes out the engine oil from the cam phaser in accordance with the ECM PWM (Pulse With Modulation) control signal,
– the CVVT Oil Temperature Sensor (OTS) which measures the engine oil temperature,
– and the Cam Phaser which changes the cam phase by using the hydraulic force of the engine oil.
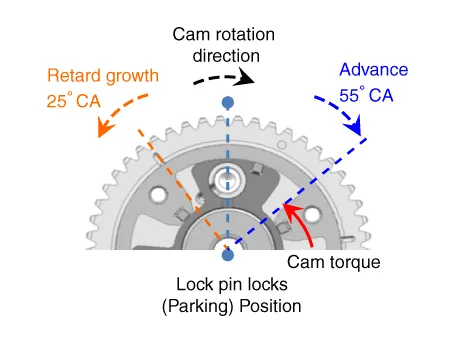
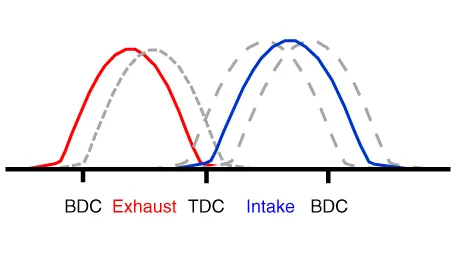
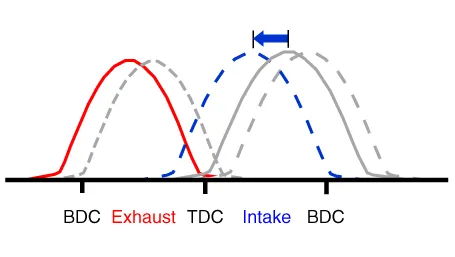
The engine oil which is supplied from the CVVT oil control valve changes the cam phase in the direction (Intake Advance/Exhaust Retard) or opposite direction (Intake Retard/Exhaust Advance) of the engine rotation by rotating the rotor connected with the camshaft inside the cam phaser.
| ▷Effect Improves fuel efficiency by approx. 1.7%. Expands the intake CVVT operating range. (Increases the retarded amount by up to 30° compared to the default state.) ∇ LIVC (Late Intake Valve Close) ∇ 1. Improves fuel efficiency by reducing pumping loss. 2. Improves knocking characteristics by reducing compression ratio. |
| |
| Default position : Middle CVVT operates in advanced / retarded directions. |

• The variable force solenoid (VFS) changes its force depending on the PWM duty to control the stroke of the OCV.
• It also controls the lock, unlock, advanced, retarded, and holding functions.
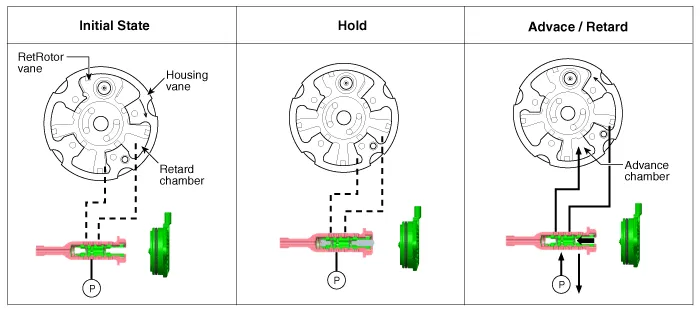
[CVVT System Mode]
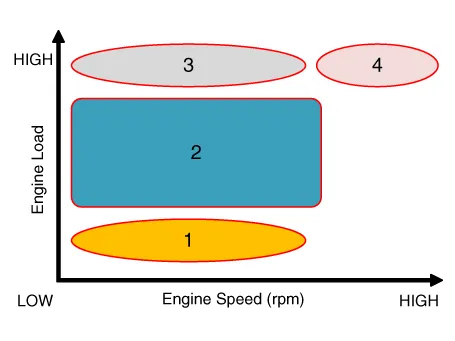
| (1) Low Speed / Low Load | (2) Part Load |
|
|
| (3) Low Speed / High Load | (4) High Speed / High Load |
|
|
| Driving Condition | Exhaust Valve | Intake Valve | ||
| Valve Timing | Effect | Valve Timing | Effect | |
| (1) Low Speed/Low Load | Completely Advance | * Valve Under-lap * Improvement of combustion stability | Middle | * Valve Under-lap * Improvement of combustion stability |
| (2) Part Load | Retard | * Reduction of HC | Retard | * Reduction of pumping loss |
| (3) Low Speed /High Load | Completely Advance | * Reduction of pumping loss | Advance | * Prevention of intake back flow (Improvement of volumetric efficiency) |
| (4) High Speed/High Load | Completely Advance | * Reduction of pumping loss | Advance | * Prevention of intake back flow (Improvement of volumetric efficiency) |
Other information:
Hyundai Accent (HC) (2017 - 2022) Service Manual: Description and Operation
- Function NoItemDescription 1Washer Linked Wiper – If the washer switch is pressed ON for 0.06 second with the vehicle mode in IGN2, the wiper relay is turned ON after washer switch ON, and then the wiper relay is turned OFF after wiper parking signal ON. 2MIST Linked Wiper – If the wiper mist switch is pressed ON for 0.6 second with the vehicle mode in IGN2, the wiper relay is turned ON, and then OFF after wiper parking signal ON.Hyundai Accent (HC) (2017 - 2022) Service Manual: Instrument cluster
â– Type A â– Type B 1. Tachometer 2. Speedometer 3. Engine coolant temperature gauge 4. Fuel gauge 5.Warning and indicator lights 6. LCD display (including Trip computer)
Contents
Categories
- Manuals Home
- Hyundai Accent Owners Manual
- Hyundai Accent Service Manual
- Questions & Answers
- Video Guides
- Useful Resources
- New on site
- Most important about car
- Privacy Policy
0.0057